
| Group | Superfamily | Family | Identified in our Lab | Identified by other Lab |
| IS630-Tc1-mariner/ITm | Tc1/mariner | DD34E/ZB and ZB like | Y | |
| DD34E/SB and SB like | Y | |||
| DD34E/Skipper (SK) | Y | |||
| DD34E/Passport | ? | |||
| DD34E/Frog Prince | ? | |||
| DD35E/Traveler (TR) | Y | |||
| DD36E/Incomer (IC) | Y | |||
| DD37E/TRT | Y | |||
| DD37E/Mosquito (MS) | Y | |||
| DD38E/Intruder (IT) | Y | |||
| DD34D/Mariner | Y (unpublished data) | |||
| DD37D/maT | Y | |||
| DD39D/Guest (GT) | Y | |||
| DD41D/Visitor (VS) | Y | |||
| pogo | Fot/Fot-like (DD35D) | Y | ||
| Passer (PS)/DD35D | Y | |||
| Tigger/DD29-36 | Y | |||
| pogoR/DD29-59D | Y | |||
| Lemi/DD29D-42D | Y | |||
| Mover/DD36E | Y | |||
| DD82E/Sailor | DD82E/Sailor | Y | ||
| DD34E/Gambol | DD34E/Gambol (GB) | Y | ||
| DD35E/Hiker (HK) | Y | |||
| IS256/DxxH | hAT | TcBuster/TB | Y | |
| Ac | ? | |||
| Tip | ? | |||
| Cleaner/CN | Y (unpublished data) | |||
| Dancer/DN | Y (unpublished data) | |||
| Roamer/RM | Y (unpublished data) | |||
| MuDR | MuDR | ? | ||
| IS1380/piggyBac | piggyBac | Pokey | Y (unpublished data) | |
| ? | ||||
| IS5/PHIS | PHIS | PIF/Harbinger | Y | |
| ISL2EU | Y | |||
| Spy | Y (unpublished data) | |||
| Pangu | Y | |||
| NuwaI | Y | |||
| NuwaII | Y | |||
| CCHH | Transib | Transib | ? | |
| EnSpm/CACTA | EnSpm/CACTA | ? |
一、转座元件 介绍
TE education: RepBase (girinst.org)
转座元件(Transposable element,TE)
转座元件(Transposable element,简称TE),又称转座子或移动元件,是一类DNA片段的集合,可以通过转座作用在基因组中从一个位置移动或复制到另一个位置。TE的长度范围从小于100个碱基对到超过20,000个碱基对不等。转座之后,很多类型TE两侧都含有短的(约1-20个碱基对)直接重复序列,这些直接重复序列是转座过程中从靶序列中衍生出来的靶位点重复序列(target site duplications,TSDs)。然而,一些TE类型,例如Helitron、几个Harbinger家族和CR1逆转座子,不产生TSDs。TSD的长度通常是一组TE及其相关物种的特征,但在不同家族和超家族中可能有所变化。在多数真核生物基因组中,TE是重复序列的主要成份。其他重复序列包括串联重复序列(卫星序列或微卫星)、零星的基因组重复以及一些多拷贝宿主基因(如rRNA、tRNA、组蛋白基因等)。事实上,TE可以被视为基因组内的寄生元件。同样地,细胞间病毒也可以被视为TE,因为它们可以整合到宿主基因组中,例如LTR-逆转录病毒。TE对宿主基因组具有多样化的进化影响。
阅读更多Transposable element – Wikipedia
转座元件
转座元件(TE),也称为转座子或跳跃基因,是DNA中的一种核酸序列,可以在基因组内改变其位置,有时会介导产生突变或逆转突变,从而改变细胞的遗传特征和基因组大小。转座往往导致相同遗传物质的复制。在人类基因组中,L1和Alu转座子是两个典型例子。巴巴拉·麦克林托克在1983年因发现转座子而获得了诺贝尔奖。 转座子在个性化医学中的重要性日益凸显;在多维大数据组学分析中,转座子也越来越受到关注。
在真核生物中,转座子占据了基因组的很大一部分,是真核细胞中DNA质量的主要决定因素。尽管转座子是自私的遗传元件,但许多转座子在基因组功能和进化中都发挥重要作用。转座子对于科学研究人员来说也非常有用,可以利用转座子对活有机体进行体内DNA遗传修饰。
转座子至少可以分为两大类:I类转座子(也称逆转录转座子),通常需要通过逆转录方式介导转座,而II类转座子(也称DNA转座子),能编码转座酶,介导转座(包括转座子在原有位置的切除和和新位置的插入),有些转座子也编码其他蛋白质。
阅读更多Copy-out–Paste-in IS elements identifed in prokaryotes
| Families | groups | Size-range | DR | Ends | IRs | Nb ORF | Frameshift | Chemistry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1 | IS1 | 740-1180 | 8-9 | GGnnnTG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE |
| ISMhu11 | 900-4600 | 0-10 | Y | 2 | ORFAB | |||
| IS3 | IS911 | 1250 | Y | 2 | ORFAB | |||
| IS150 | 1200-1600 | 3-4 | TG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE | |
| IS407 | 1100-1400 | 4 | TG | |||||
| IS51 | 1000-1400 | 3-4 | TG | |||||
| IS3 | 1150-1750 | 3-4 | TGa/g | |||||
| IS2 | 1300-1400 | 5 | TG | |||||
| IS481 | – | 950-1300 | 4-15 | TGT | Y | 1 | ||
| IS30 | – | 1000-1700 | 2-3 | Y | 1 | DDE | ||
| IS110 | IS110 | 1200-1550 | 0 | N | DEDD | |||
| IS1111 | Y * | DEDD | ||||||
| IS256 | – | 1200-1500 | 8-9 | Ga/g | Y | 1 | DDE | |
| ISL3 | – | 1300-2300 | 8 | GG | Y | 1 | ||
| IS21 | – | 1750-2600 | 4-8 | TG | Y | 2 * | DDE | |
| ISLre2 |
Classification, terminal features, TSD features and the number of entries of DNA transposons in Repbase
| Group | Superfamily | Termini | Mechanism | TSD | Entries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS630/Mariner | Mariner/Tc1 | YR..YR | Cut-and-paste | TA | 2,539 |
| Zator | GG..CC | Cut-and-paste | 3 | 54 | |
| IS481/Ginger | Ginger1 | TGT..ACA | Cut-and-paste | 4 | 39 |
| Ginger2/TDD | TGT..ACA | Cut-and-paste | 4–5 | 20 | |
| IS3/IS3EU | IS3EU | TAY..RTA | Copy-out–Paste-in? | 6 | 23 |
| IS1016/Merlin | Merlin | GG..CC | Cut-and-paste | 8–9 | 75 |
| IS256/DxxH | hAT | YA..TR | Cut-and-paste | 5–8 | 2,955 |
| MuDR | GR..YC | Cut-and-paste | 8–9 | 1,345 | |
| P | CA..TG | Cut-and-paste | 7–8 | 189 | |
| Kolobok | RR..YY | Cut-and-paste | TTAA | 286 | |
| Dada | ? | 6–7 | 36 | ||
| IS1380/piggyBac | piggyBac | YY..RR | Cut-and-paste | TTAA | 377 |
| IS5/PHIS | Harbinger | RR..YY | Cut-and-paste | 3 | 1,097 |
| ISL2EU | RR..YY | Cut-and-paste? | 2 | 88 | |
| Spy | Cut-and-paste | no | |||
| NuwaI | |||||
| NuwaII | |||||
| Pangu | |||||
| CCHH | EnSpm/CACTA | CAC..GTG | Cut-and-paste | 2–4 | 715 |
| Transib | CAC..GTG | Cut-and-paste | 5 | 123 | |
| KDZP | Zisupton | ? | ? | 8 | 18 |
| Sola | Sola | Cut-and-paste | |||
| Sola1 | ? | Cut-and-paste | 4 | 100 | |
| Sola2 | GRG..CYC | Cut-and-paste | 4 | 90 | |
| Sola3 | GAG..CTC | Cut-and-paste | TTAA | 28 | |
| Unclassified Sola | Cut-and-paste | 1 | |||
| ? | Academ | YR..YR | Cut-and-paste | 3–4 | 90 |
| ? | Novosib | CA..TG | Cut-and-paste | 8 | 9 |
| Crypton | Crypton | Copy-out–Paste-in | |||
| CryptonF | Copy-out–Paste-in | 0 | 23 | ||
| CryptonA | TTA.. | Copy-out–Paste-in | 0 | 17 | |
| CryptonI | ? | Copy-out–Paste-in | 0 | 9 | |
| CryptonS | TATGG.. | Copy-out–Paste-in | 0 | 59 | |
| CryptonV | ? | Copy-out–Paste-in | 0 | 46 | |
| Unclassified Crypton | Copy-out–Paste-in | 80 | |||
| Helitron | Helitron | TC..CTRR | Rolling circle | 0 | 955 |
| Polinton | Polinton | AG..CT | Self-synthesizing | 6 | 108 |
| Unclassified DNA transposon | 2,357 | ||||
| Total | 13,960 |
Eukaryotic cut-and-paste transposase superfamilies
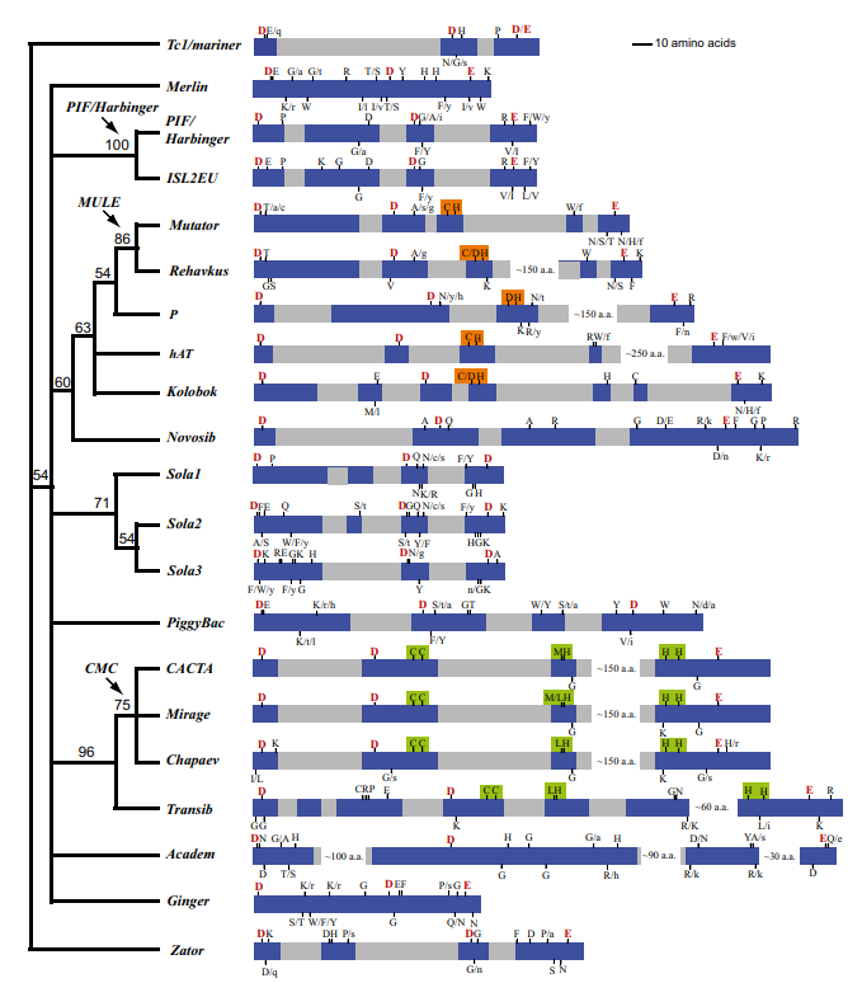
Fig. 2. An unrooted consensus tree of the transposase superfamilies inferred from the presence or absence of the highly conserved residues in the signature strings. Bootstrap values are at the nodes. The arrows with labels indicate superfamily clusters merged in our revised classification. Shown on the right is a schematic representation of the DDE/D domain and the signature string for each superfamily. Conserved blocks are highlighted in blue, variable regions are in gray. White gaps are regions not drawn to scale. The DDE triads are highlighted in red. Alternative residues are marked by slashes; lowercase indicates that a residue occurs in <10% of the sequences in the alignment profile. The C/DH motif is highlighted in orange; the C(2)C, [M/L]H, and H(3-4)H motifs are highlighted in green.
List of Copy-out–Paste-in IS elements
List of mobile elements whose transposases have been examined by secondary structure prediction programs
| Family | Element (or protein) analyzed | Active or # copies in genome1 | From secondary structure, type of DDE/D motif2 | Relevant references3 |
| IS1 | IS1NISSto9 | >40*5 | DD(24)EDD(20)E | * Nyman et al., 1981; Ohta et al., 2002, 2004; Siguier et al., 2009 |
| IS1595 | 1. ISPna2 | ?,DD(36)N” | Siguier et al., 2009 | |
| 2. ISH4 | ?,DD(36)E” | Siguier et al., 2009 | ||
| 3. IS1016C | ?,DD(34)E” | Siguier et al., 2009 | ||
| 4. IS1595 | ?,DD(35)N” | Siguier et al., 2009 | ||
| 5. ISSod11 | 13 | DD(34)H | Siguier et al., 2009 | |
| 6. ISNWi1 | ?,DD(35)E” | Siguier et al., 2009 | ||
| 7. ISNha5 | ?,DD(33)E” | Siguier et al., 2009 | ||
| Merlin: MERLIN1_SM | Consensus | DD(36)E | Feschotte, 2004 | |
| IS3 | IS911 | Active | DD(35)E | Polard and Chandler, 1995; Rousseau et al., 2002 |
| IS481 | IS481 | ?00* | DD(35)E | *Glare et al., 1990; Chandler and Mahillon, 2002 |
| IS4 | IS50R | Active | PDB ID: 1muhDD(-strand)E | Rezshazy et al., 1993; Davies et al., 2000 |
| IS701 | IS701ISRso17 | Active (15*)7 | DD(-strand)E | *Mazel et al., 1991 |
| ISH3 | ISC1359ISC1439A | 513 | DD(-strand)E | |
| IS1634 | IS1634ISMac5ISPlu4 | Active (?0*)77 | DD(-strand)E | *Vilei et al., 1999 |
| IS5 | IS903 | Active | DD(65)E | Derbyshire et al., 1987; Rezshazy et al., 1993; Tavakoli et al., 1997 |
| PIF/Harbinger: PIFa (Z. mays) | Active | DD(59)E | Zhang et al., 2001; Kapitonov and Jurka, 2004; Sinzelle et al., 2008 | |
| IS1182 | IS660ISPsy6 | 314 | DD(-strand)E | Takami et al., 2001 |
| IS6 | IS6100 | Active | DD(34)E | Martin et al., 1990; Mahillon and Chandler, 1998 |
| IS21 | IS21 | Active | DD(45)E | Mahillon and Chandler, 1998; Berger and Haas, 2001 |
| IS30 | IS30 | Active | DD(33)E | Caspers et al., 1984; Mahillon and Chandler, 1998 |
| IS66 | IS679ISPsy5ISMac8 | Active333 | DD(-helical?)E | Han et al., 2001 |
| IS110 | IS492IS1111 | Active20 | DEDDDEDD | Perkins-Balding et al., 1999; Buchner et al., 2005 |
| IS256 | IS256 | Active | DD(-helical)E | Mahillon and Chandler, 1998; Prudhomme et al., 2002 |
| MuDr/Foldback (Mutator) | Active | DD(-helical)E | Eisen et al., 1994; Babu et al., 2006; Hua-Van and Capy, 2008 | |
| IS630 | ISY100 | Active | DD(34)E | Doak et al., 1994; Feng and Colloms, 2007 |
| Tc1/mariner: Mos1 (D. mauritiana) | Active | PDB ID: 2f7tDD(34)D | Plasterk et al., 1999; Richardson et al., 2006 | |
| Zator: Zator-1_HM | 36* | DD(43)E | *Bao et al., 2009 | |
| IS982 | ISPfu3 | 5 | DD(47)E | Mahillon and Chandler, 1998 |
| IS1380 | IS1380A | ?00* | DD(-strand)E | *Takemura et al., 1991; Chandler and Mahillon, 2002 |
| piggyBac (T. ni) | Active | DD(-strand)D | Cary et al., 1989; Sarkar et al., 2003; Mitra et al., 2008 | |
| ISAs1 | ISAzo3 | 7 | DD(-strand)E/D? | |
| ISL3 | IS31831IS651 | Active22 | DD(-helical)E | Suzuki et al., 2006 |
| Tn3 | Tn3 (E. coli) | Active | DD(-helical?)E | Grindley, 2002 |
| hAT | Hermes (M. domestica) | Active | PDB ID: 2bw3 DD(-helical)E insertion | Warren et al., 1994; Rubin et al., 2001; Hickman et al., 2005 |
| CACTA | CACTA1 (A. thaliana) En/Spm ZM | Active | DD(-helical?)E/D? | Miura et al., 2001; DeMarco et al., 2006 |
| P | Drosophila | Active | ? | Rio, 2002 |
| Transib | Transib1_AG | Consensus | DD(-helical)E | Kapitonov and Jurka, 2005; Chen and Li, 2008 |
| RAG1 (M. musculus) | Active | DD(-helical)E | Kim et al., 1999; Landree et al., 1999; Lu et al., 2006 | |
| Sola | Sola3-3_HM | Multiple copies* | DD(40)E | *Bao et al., 2009 |
Hickman AB, Chandler M, Dyda F. Integrating prokaryotes and eukaryotes: DNA transposases in light of structure. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Feb;45(1):50-69. doi: 10.3109/10409230903505596.
Classification, distribution and the number of entries of LTR retrotransposons in Repbase
| Superfamily | Total |
|---|---|
| Copia | 10,595 |
| Gypsy | 6,694 |
| BEL | 1,855 |
| ERV | |
| ERV1 | 1,967 |
| ERV2 | 1,266 |
| ERV3 | 657 |
| ERV4 | 187 |
| Lentivirus | 4 |
| Unclassified ERV | 325 |
| Unclassified LTR | 719 |
| DIRS | 418 |
Classification, and the number of entries of non-LTR retrotransposons in Repbase
| Group | Clade | Total |
|---|---|---|
| CRE | CRE | 43 |
| R2 | R4 | 46 |
| Hero | 23 | |
| NeSL | 106 | |
| R2 | 159 | |
| Dualen | RandI/Dualen | 13 |
| L1 | Proto1 | 6 |
| L1 | 1,690 | |
| Tx1 | 273 | |
| RTE | RTETP | 1 |
| Proto2 | 47 | |
| RTEX | 138 | |
| RTE | 487 | |
| I | Outcast | 23 |
| Ingi | 17 | |
| Vingi | 141 | |
| I | 195 | |
| Nimb | 108 | |
| Tad1 | 141 | |
| Loa | 74 | |
| R1 | 237 | |
| Jockey | 243 | |
| CR1 | Rex1 | 95 |
| CR1 | 803 | |
| Kiri | 91 | |
| L2 | 285 | |
| L2A | 5 | |
| L2B | 27 | |
| Crack | 140 | |
| Daphne | 227 | |
| Ambal | Ambal | 8 |
| Penelope | Penelope | 477 |
| SINE | SINE1/7SL | 95 |
| SINE2/tRNA | 539 | |
| SINE3/5S | 30 | |
| SINEU | 17 | |
| Unclassified SINE | 112 | |
| Unclassified non-LTR retrotransposon | 179 | |
| Total | 7,341 |
Reference: Kenji K. Kojima, Structural and sequence diversity of eukaryotic transposable elements, Genes & Genetic Systems, 2019, Volume 94, Issue 6, Pages 233-252
Proposal of TE classes with some members having a DNA transposon phenotype

Reference: Benoît Piégu, Solenne Bire, Peter Arensburger, Yves Bigot, A survey of transposable element classification systems – A call for a fundamental update to meet the challenge of their diversity and complexity,
Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, Volume 86, 2015, Pages 90-109,
ISSN 1055-7903, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.03.009.
Major Features of Prokaryotes IS families (ISfinder)

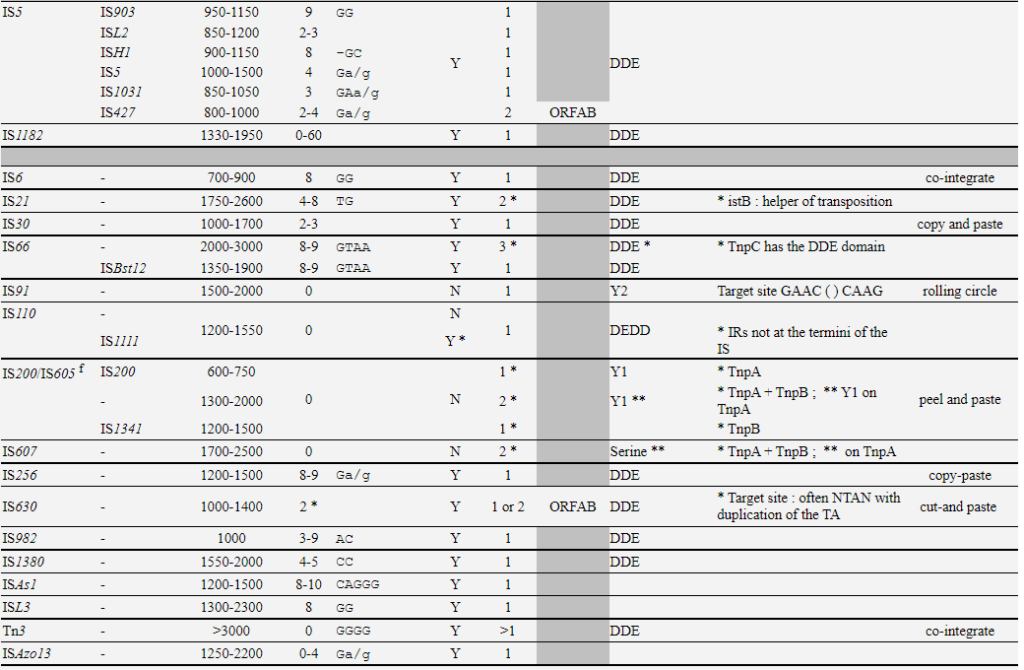
Overview of common transposon annotation tools
| Approach | Class I | Class II | ||||||||
| Name | Novo. | Struc. | Simil. | LTR | LINE | SINE | TIR | HEL | MITE | |
| RepeatMasker | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| RepeatModeler | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| CLARI_TE | (107) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| TESeeker | (41) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| PILER | (40) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Censor | (108) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| RepLong | (109) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| EDTA | (44) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| MGEScan | (110) | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| LTR_Finder | (111) | x | x | |||||||
| LtrDetector | (112) | x | x | |||||||
| LTRpred | (73) | x | x | x | x | |||||
| LTRharvest | (66) | x | x | x | x | |||||
| LTRdigest | (113) | x | x | |||||||
| SINE-Finder | (68) | x | x | x | ||||||
| SINE-Scan | (69) | x | x | x | ||||||
| TIRvish | (67) | x | x | |||||||
| HelitronScanner | (42) | x | x | |||||||
| MUSTv2 | (70) | x | x | |||||||
| MiteFinderII | (71) | x | x | |||||||
| MITE-Tracker | (72) | x | x | |||||||
| detectMITE | (45) | x | x | |||||||
| MITE-Hunter | (47) | x | x | |||||||
| TransposonUltimate | ||||||||||
Distribution of TEs across the eukaryote phylogeny

TE keynote lectures
*Part 1: Introduction to transposable elements (38 minutes) by Susan Wessler
*Part 2: How transposable elements amplify throughout genomes (70 minutes) by Susan Wessler
*Transposable Element-mediated Structural Variation: From McClintock to Pangenomes – YouTube by Susan Wessler, department of Botany and Plant Sciences, University of California (55 minutes)
The Dynamic Genome: Unintelligent Design – YouTube by Susan Wessler department of Botany and Plant Sciences, University of California (60 minutes)
LINE1 by Haig Kazazian Jr – YouTube 43′
CARTA: Comparative Anthropogeny – LINE1 Retrotransposons – YouTube 21′
* Understanding the Strategies Evolved by a Very Successful Transposable Element by Dr. Susan Wessler – YouTube department of Botany and Plant Sciences, University of California 80 minutes
*All roads lead to transposons: Dr. Cedric Feschotte, Cornell UniversityCornell University – YouTube (38 minutes)
*Transposon site-specificity and genome evolution – Allan Spradling – YouTube (50 minutes)
*EMBL Keynote Lecture – Germline reprogramming and epigenetic inheritance of transposable elements – YouTube Robert Martienssen, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, USA (68 minutes)
*Transposable elements, DNA methylation and transgenerational epigenetics, lessons from plants – YouTube Vincent Colot – Institut de Biologie de l’École Normale Supérieure (IBENS) – CNRS (58 munutes)
*Jumping Genes Lead the Way – YouTube by Uwe Hilgert, DNA learning center, University of Arizona (60 minutes)
*LINE impact: CGC Webinar Series – June 2021 – YouTube 58 minutes
Vir_S14_L15 Retroviruses – YouTube 64′
*Unit8C Transposable Elements – YouTube, 20 minutes
CSHL Keynote Series, Junk Evolution: Dr Andrew Clark, Cornell University – YouTube 54 minutes
*Retroelements: YouTube (85minutes)
Chemistry of Life Part – YouTube 43 minutes
Lecture 1 (2021) How transposable elements amplify throughput genomes by Ruslan Kalendar, plants, University of Helsinki (40 minutes)
Barbara McClintock’s Controlling Elements, Then and Now – YouTube (60 minutes)
Machine Learning in Bioinformatics: Understanding Transposable Elements – YouTube (20 minutes)
Accelerated Evolution by Diversity-Generating Retroelements – Jeff Miller – YouTube (28 minutes)
The Jumping Genome: Changing Ideas about Heredity and Evolution – YouTube (75 minutes)
*CSHL Keynote, Retrotransposon storm hypothesis of ALS—The dangers of a Collyer’s genome Dr. Josh Dubnau, Stony Brook School of Medicine – YouTube (40minutes)
TE lectures
DNA Interest Group Event: Transposable Elements- The “Ghosts” in Our DNA – YouTube (52 minutes)
EMBL Keynote Lecture – The Nucleosome: Guardian and Gateway to Genomes – YouTube (60 minutes)
SEEM 2022 01 14 Yann Bourgeois: “Studying the population dynamics of transposable elements” – YouTube (50minutes)
Transposable element activation in Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies │Dr Bess Frost – YouTube (60 minutes)
How Can Transposons Accelerate Your Genomics Research? (50 minutes)
Unit8C Transposable Elements – YouTube (20 minutes)
CGM79期:区树俊 Bench-marking transposable element annotation methods – YouTube (中文,48minutes)
Lee Kass – “Barbara McClintock at Cornell university: 1919-1939 & Beyond” – YouTube (50 minutes)
*Your Genomic Parasites – YouTube (45 minutes)
Transposons / Transposable elements explained (20 minutes)
Introduction to Transposons (7 minutes) by Nicole Lantz
Plasmids and Transposons (26 minutes)
DNA Tn
2025年11月19日Transposase- Based Genome Editing: Advantages and Delivery to Treat Retinal Genetic Disease
2025年2月8日Molecular innovation at the CRISPR-transposon interfaceSamuel H. Sternberg, PhD
2024年8月13日Mechanistic insights into RNA-guided DNA integration using transposons – YouTube
2024年8月27日De novo gene synthesis by an antiviral reverse transcriptase
2024年12月11日 CSHL Keynote, Dr. Zhang, MIT/Broad Institute
2024年5月17日 ELTE TTKZoltán Ivics (biochemist) honorary doctorate lecture at ELTE
2023年12月2日Leveraging Programmable CRISPR-Associated Transposases for Next-Generation Genome Engineering
2022年3月15日 Faculty Talk Series | Prof. Zoltan Ivics
2021年1月13日 R in D – Research in Germany: Prof. Zoltan Ivics on the Sleeping Beauty Transposon
2020年6月10日 ESGCT e-School: The Sleeping Beauty transposon – a molecular parasite tamed for genome engineering
2017年11月27日 ESGCT 2017 Education Day – Zsuzsanna Izsvak
piggyBac Transposons to Cut and Paste DNA (28 minutes) by Lauren E. Wooddard
PiggyBac Applications: Beyond Stable Cell Lines – YouTube (20 minutes)
2023年4月4日Memory rich CAR T cell engineering by piggyBac transposon system for solid malignancies
2023年11月29日02 Development and clinical application of piggyBac-based CAR-T cells for hematological malignancies
2023年8月3日Webinar – Optimizing Gene Expression with Bioluminescence & the piggyBac System
2022年5月25日A cGMP Compatible, Non-Viral CAR T Cell Manufacturing Process
2022年6月7日PiggyBac Applications: Beyond Stable Cell Lines
Faculty Talk Series | Prof. Zoltan Ivics – YouTube 60 minutes
ESGCT e-School: The Sleeping Beauty transposon – a molecular parasite tamed for genome engineering – YouTube (56 minutes)
RTn
Role of transposons in brain and learning processes | Dr. Peter Borger | EN – YouTube (55 minutes)
Daniel Caffrey – Evolution of Alu elements in long non coding RNA and mRNA – YouTube (45 minutes)
CARTA: Comparative Anthropogeny – LINE1 Retrotransposons – YouTube (21 minutes)
Lec 2.8.1 Alu Transposon – YouTube (20 minutes)
RNA Transposons (15 minutes)
Gene editing
2025年11月19日Advances and limitations of in vivo viral delivery systems for therapeutic gene editing (April 16)
2025年3月28日Treating relapsed and refractory disease focusing on Car T-cell therapy
2025年12月4日Advanced Gene Therapy Development Solutions A Comprehensive Platform for Next Generation Therapeutic
2025年12月2日Gene Editing Approaches
2025年5月19日Genome modeling and design across all domains of life with Evo 2 – YouTube
2024年7月11日Engineering highly active and diverse nuclease enzymes by ML and high-throughput screening
2024年11月26日Rapid protein evolution by few-shot learning with a protein language model
2025年4月17日AI-EVOLVEpro: Webinar: Programmable Molecular Tools for Biology and Genome Editing
2024年5月9日Design of highly functional genome editors by modeling the universe of CRISPR-Cas sequences
2025年10月11日WEBINAR: Global Overview of Gene Editing in Pigs
2025年11月14日CRG-AS-001: A Non-Viral Delivered CRISPR Gene Editing Approach for AS: From Bench to Bedside
2025年9月29日Cancer, Cancer Genomes, and Genome Editing | Dr. Lincoln Stein, MD PhD
2025年11月9日Cas-CLOVER vs. CRISPR | Advancing Genome Editing Precision for Biologics
2025年11月7日Advance Your Cell Therapy with Innovative CRISPR & mRNA-LNP Tools
2025年11月12日3000788 Fall 2025 L26 – Synthetic biology – YouTube
2025年11月20日Epigenome editing in CAR T cells (March 19) – YouTube
2025年10月28日Engineering Tomorrow’s Rodent Models: Evolving Knock-In Approaches
2025年11月19日Advances and limitations of in vivo viral delivery systems for therapeutic gene editing (April 16)
2025年3月8日Advancing Gene Editing Strategies for Efficient Genetic Improvements in Animal Models
2025年4月26日Virginijus Siksnys – Keynote at CRISPRMED25 – YouTube
2025年4月8日Dr. Thomas Forbes – Gene Editing (Session 5)
2025年7月11日The Scientist Symposium: The Future of CRISPR – YouTube
2025年5月4日: The Future of Genetic Engineering. #sciencedocumentary
2025年7月16日: CTSI Distinguished Speaker Series | Patrick Hsu
2024年4月18日WALS NIH Director’s Lecture: The Future of CRISPR: What’s Ahead for Genome Editing
*2024年10月5日Gene Editing: A 2024 Update with Dr. Ilya Finkelstein and Dr. Stephen C. Ekker
*2024.5.9Design of highly functional genome editors by modeling the universe of CRISPR-Cas sequences
2024年6月28日Dr. Michael Lohuis – Gene Editing for Livestock
2024年9月28日A Diverse and Efficient Approach to CRISPR Technology
2024年6月24日The Ethical Dilemma Of Genome Editing | The CRISPR Revolution
2024年9月23日How to Create Effective Vectors for Gene Delivery – YouTube
2024年4月10日Basics of In Vitro Transcribed (IVT) mRNA from Design to Therapy – YouTube
2024年10月26日Advancing Gene Delivery of Large Knockins for Rodent Animal Models
2025年9月2日Choosing, Designing, and Optimizing AAV Vectors for Research and Therapies
2024年5月3日AAV capsid discovery and design – novel sequencing approaches
2024年11月15日Powerful Directed Evolution Platform for Novel AAV Vector Discovery
2024年1月23日VectorBuilder Seminar: AAV Capsid Evolution
2023年5月23日Designing and Executing Prime Editing Experiments in Mammalian Cells – YouTube
2021年5月28日2021 Edward Novitski Prize: Feng Zhang
2024年11月26日Unlocking CRISPR Advances in Base Editing, Prime Editing and Future Applications
*2020年2月20日 GLASGOWGENE EDITING EXPLAINED! – A comprehensive guide to the principles, methods and technologies!
2017Jennifer Doudna: CRISPR Basics
2016Genome Editing in the Clinic — Dr. Michael Holmes (2016 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2016 CRISPR Applications in Human Stem Cells — Dr. Dirk Hockemeyer (2016 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2016: CRISPR Bioinformatics — Dr. Jacob Corn (2016 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2016Background on Genome Editing — Dr. Dana Carroll (2016 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015Genome editing with Cas9 RNP — Dr. Dana Carroll (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop) – YouTube
2015: CRISPR-Cas9: From Biology to Transformative Technology — Jennifer Doudna (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015 CRISPR Biology: From Discovery to Application — Dr. Jennifer Doudna (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015Applications of Inactive Cas9 — Dr. Jonathan Weissman (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015CRISPRs in Drosophila — Dr. Dana Carroll (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015 CRISPR Applications in Livestock — Dr. Scott Fahrenkrug (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015Zebrafish and CRISPR — Dr. Randy Peterson (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015CRISPR Applications in Plants — Dr. Dan Voytas (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015 Design Strategies for CRISPR Genome Editing with ssODNs — Dr. Greg Davis (2015 IGI CRISPR Workshop)
2015 Chemically Synthesized Modified Guide RNAs Enhance CRISPR-Cas Genome Editing — Laurakay Bruhn (2015)
2024年11月12日Advanced solutions for CRISPR gene editing
2024年2月4日: The Rise Of Genetic Engineering | Gene-Editing Technology | Science Documentary
2024年7月13日: “Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA” – YouTube
2024年11月10日CRISPR KO vs CRISPR KI experiment using CRISPR-Cas9
2024年4月18日Jennifer Doudna: The Future of CRISPR: What’s Ahead for Genome Editing
2024年11月20日:How to optimize non-viral CRISPR HDR for high-efficiency large knock-in in primary T cells and iPSCs*
2024年10月16日 Boost CRISPR Editing Efficiency Using Optimized sgRNA and HDR Template Design
2024年8月26日CPHR Seminar Series – David Liu
2023年5月23日Designing and Executing Prime Editing Experiments in Mammalian Cells
2023年11月17日David Liu: Base Editing and Prime Editing (Correcting Mutations that Cause Genetic Disease)
2023年12月14日Enabling GMP Production of sgRNA for CRISPR-Based Cell and Gene Therapies
2023年12月2日:Leveraging Programmable CRISPR-Associated Transposases for Next-Generation Genome Engineering
2023年10月26日Unveiling the potential of CRISPR: A guide to gene editing
2023年9月14日: From CRISPR-Cas to Tas (transposon-associated proteins) – Professor Virginijus Šikšnys
2023年3月22日[Keynote Session] The future of CRISPR Technology
2023年6月17日: Discovery and development of CRISPR-associated transposases for next-generation genome engineering
2023年11月30日Jennifer Doudna: Clare Hall King Lecture 2023 – Jennifer Doudna
2020年4月17日Alt-R HDR Design Tool & Templates
2020年8月18日Base Editing: Putting Precision into Genomic Medicine – YouTube
2020年2月25日: A Workflow for Knock-in Genome Editing: Simplified
2020-2: GENE EDITING EXPLAINED! – A comprehensive guide to the principles, methods and technologies!
2020年12月1日Novel CRISPR Knock-In Technology for the Robust Analysis of Cells and Tissue
2018-3:How to use CRISPR Cas9 for knockout, knock in and gene activation
2018年10月15日Webinar: Strategies to Efficiently Generate CRISPR KO/KI Cell Lines
*2017年3月17日:Getting started with CRISPR: a review of gene knockout and homology-directed repair
Jennifer Doudna: Jennifer Doudna: CRISPR Basics
Targeted DNA integration without double strand breaks using CRISPR RNA guided transposons – YouTube 30′
Stanford Webinar – CRISPR – 10 Years of Genome Editing and More – (60 minutes)
2022 FUTURES Gene Therapy and Gene Editing Symposium Brunch – YouTube (80 minutes)
CMB Journal Club: Genome Editing – YouTube, 21 minutes
Saturation Genome Editing in RAD51C – YouTube 24 minutes
Scientist Stories: George Church, The Future of the Genome Editing Revolution – YouTube 80 minutes
*MIT: Rewriting DNA: Big Returns from Gene Editing – YouTube 83
Basic Principles of Genome Editing – YouTube 84
Lec 10: Basics of Zinc Finger Nucleases – YouTube, 51′
MIT CompBio Lecture 24 – Genome Engineering – YouTube, 80′
Zinc fingers: From gene switches to gene therapy – YouTube, 76
Engineered zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) for the regulation of gene expression – YouTube 68
Giving Evolutionary Biologists the (Zinc) Finger – YouTube 80
Genome Editing with Engineered Zinc Finger Proteins – Philip D. Gregory – YouTube 40
Genome Editing – Shawn Burgess – YouTube 40
Lecture 7 Leucine Zipper motifs – YouTube 23
Company:Caring cross
*2026年1月6日
Alliance for Regenerative Medicine Board Vote and Welcome Remarks
Expediting the Development of Cell and Gene Therapy
Science Slam: Advancing the Frontier of T Cell Therapy in Oncology and Rheumatology
*Investing in Innovation: Advancing Gene Editing Solutions for Cystic Fibrosis
*I-CreI: Precision BioSciences
2023年11月30日:chRDNA/CRISPR hybrid RNA-DNA guided: *Caribou Biosciences
2023年11月30日Chroma Medicine
2023年8月17日Update on CAR T-Cell Therapy | LRF Webinars
2025年12月4日Advanced Gene Therapy Development Solutions A Comprehensive Platform for Next Generation Therapeutic
2025年11月9日 Multiplexing with Accuracy | Cas-CLOVER CHO Platform Innovations for Next-Gen Biologics
2025年11月9日Cas-CLOVER vs. CRISPR | Advancing Genome Editing Precision for Biologics
2025年11月9日Cas-CLOVER + Harbor-IN | License-Free Transposase Solutions for Commercial Cell Line Development
2025年10月7日:NanoCell Novel Non-Viral DNA-based Gene Therapy Vector for CAR T Engineering In Vivo
2025年5月13日:Building the Next Generation of Cell Therapies – YouTube
2025年5月13日:Ex vivo and In vivo CRISPR Editing to Reprogram T Cells
2025年5月18日:The Future of In Vivo CAR-T
2025年3月15日:Aberrantly spliced tumor epitopes: lost and found
2025年3月18日:CARTCell Targeting Enhancements – YouTube
2025年3月24日:Treatment Strategies Targeting Hemophilia A – YouTube
2025年5月18日:Genetic Therapy in Sickle Cell Disease: Targeting BCL11A with Lentivirus shmiR
2025年3月13日:Exploring CAR-T cell therapy and Auto-immune Diseases – YouTube
2025年3月12日:Policy and Business Innovation for Broader Access to Genetic Medicines
2025年5月21日:The Importance of Public Benefit Corporations in Rare Disease Gene Therapy
2025年4月8日:Innovative Payment Models in Cell/Gene Therapies
2025年3月12日:Federal impacts to CGTx
6-2025年3月15日:Commercial Challenges to Gene Editing – YouTube
9-2025年3月13日:Bottom-Up Approach to Improve Patient Access for Genetic Medicine
2025年12月2日Gene Editing Approaches
2026年1月13日Dr. Andras Heczey, CAR-T Cell Trials
2024年10月10日:Genome Engineering for Rare Diseases, 2024
2024年10月30日:Advancing the Development of Gene Therapy for Rare Diseases Center for Individualized Medicine 2024
2024年11月13日:The Precision and Flexibility of Homologous Recombination-Based Genome Editing
2025年12月20日 Plenary Session: The future of Gene Therapy in Inherited Blood Disorders
2025年12月17日 Progress toward a cure for hemophilia: gene editing explained
2025年10月6日Around the World: Oncology, Hematology, and Cancer-Focused Cell and Gene Therapy in India
2023年11月30日 Capstan Therapeutics
Gene therapy
*2025年12月4日Advance Your Cell Therapy With Innovative CRISPR & mRNA LNP Tools
2025年12月11日Biotech Connector: Innovations Shaping the Future of Cell and Gene Therapy – YouTube
2025年12月17日Progress toward a cure for hemophilia: gene editing explained
2025年12月12日Webinar: Virus-Free Gene Modification with Minicircle DNA for Advanced Therapies – 10.12.2025
2025年12月5日Topic1: Lentiviral Vector Process Development for In Vivo CAR-T: Key Points and Core Challenges
2025年4月14日CAR-T Cell Therapy: Origins and New Directions | Michel Sadelain | Immunoschool 2025
2025年6月6日Webinar: Tools to Advance CAR-T and TCR-T Cell Therapy Development
*2025年10月7日Novel Non-Viral DNA-based Gene Therapy Vector for CAR T Engineering In Vivo – YouTube
2025年11月15日A genome engineering toolbox for HSCs
2025年8月9日The Power of CAR-T Therapy with Dr. Carl June @ The Cure JM Family Conference
2025年5月1日Genetic Engineering of Human Stem Cells and Regulatory T Cells
2024年10月30日Advancing the Development of Gene Therapy for Rare Diseases Center for Individualized Medicine 2024
2024年4月15日Gene Editing Technologies: Transforming Rare Disease Care
2024年1月28日CAR-T Cell Therapy: A New Chapter in Lupus Treatment? – YouTube
2024年10月30日Lupus Ontario Symposium 2024 – CAR T-Cell Therapy and Upcoming Treatments
2024年11月12日CAR T-cell Therapy: An Emerging Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases
2024年11月13日The Precision and Flexibility of Homologous Recombination-Based Genome Editing – YouTube
2023年8月1日Gene-editing Technologies: Powerful Tools Rewriting the Code of Life
2023年12月5日How to Create CRISPR-Edited T Cells More Efficiently for Tomorrow’s Cell Therapies
2022年2月8日 ESGCT e-Seminar: Virus-free gene editing of T cells
2021年5月1日Updates in CAR T Cell Therapies
2021年7月29日CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing for autologous CAR-T cell production
2020年12月16日ESGCT e-School: Cancer immunotherapy: beyond CAR T cells
2020年5月6日ESGCT e-School: Gene Therapy – From Concept to Proof
2020年7月22日ESGCT e-School: Knock-out, Knock-in, repair or regulate – the tool-box of designer nucleases
2020年7月29日ESGCT e-School: Nucleases used for gene editing
2021年2月10日Toni Cathomen, University of FreiburgESGCT e-Seminars: Safety considerations in therapeutic genome editing
2021年2月17日ESGCT e-Seminars: Intellia’s Modular CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Platform for the Treatment of Disease
2020年5月6日ESGCT e-School: Gene Therapy – From Concept to Proof – YouTube
2020年6月16日 A CRISPR Vision for the Future of Cell Therapy
Gene Therapy (60 minutes)
ESGCT 2017 Education Day – Zsuzsanna Izsvak – YouTube 30 minutes
Evolution of AAV Vector for Gene Therapy – YouTube (30 minutes)
April 2022 Cure SMA and Novartis Gene Therapies Clinical Trial Update Webinar – YouTube (45 minutes)
Gene Therapy Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow (60 minutes)
The Science Behind Gene Therapy – (60 minutes)
Gene Therapy: Getting Up to Speed (40 minutes)
Cancer Gene Therapy 2.0: Immunotherapy for Cancer (60 minutes)
Gene Therapy Manufacturing Workshop –(60 minutes)
Manufacturing of Cell-Based Therapies – (50 minutes)
New Innovations in Cell Therapy – (80 minutes)
Gene Therapy Explained (4.30 minutes) by AGTC company
Gene Therapy Basics (4 minutes)
The Basics of Gene Therapy – (5 minutes) by Roche
Gene therapy is the future of medicine (10 minutes) by Dr. Nafiseh Nafissi
2022 WMIF: Non-viral Vectors for Gene Therapy (60 minutes)
Nanoparticle Gene Delivery (1.28 minutes) by Johns Hopkins Institute
The history of the cell, cell therapy, gene therapy, and more (120 minutes)
From the Human Genome Project to Precision Medicine: A Journey to Advance Human Health – Eric Green – YouTube (100 minutes)
Benchling Webinar: Codon Optimization (50 minutes)
Prof. Katalin Karikó「Developing mRNA for therapy」 – YouTube 32′
Non-viral-CAR-T
2025年10月7日Novel Non-Viral DNA-based Gene Therapy Vector for CAR T Engineering In Vivo
2025年12月4日Next Generation Genetic Discovery Systems in Human Immune Cells
2025年6月22日Establishing a Non-Viral Manufacturing Process for Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Therapies
2024年12月17日Unleashing the Power of Non-Viral Gene Editing: Transforming Cell Therapy Development with Live Q&A
2024年11月8日Non-Viral CRISPR Knock-In Anti-B7-H3 CAR-T Cells for the Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer
2023年11月28日05 Non-viral CRISPR CAR-T cells going viral
2024年11月20日How to optimize non-viral CRISPR HDR for high-efficiency large knock-in in primary T cells and iPSCs
2023年11月22日A Next-Generation Plasmid Demonstrated to Improve Non-Viral Vector Manufacturing – Nanoplasmidᵀᴹ
2023年11月29日03 International collaboration of CAR-T cell therapy using non-viral vector system
2023年5月12日Laura Sepp Lorenzino: The Promise of CRISPR Therapeutics In Vivo and Cell Therapy Applications
2023年9月28日GenScript Webinar – Unlocking the Future of Cell Therapy: Non-Viral Gene Editing Revealed!
2022年5月25日A cGMP Compatible, Non-Viral CAR T Cell Manufacturing Process
2022年2月9日Non-viral T cell engineering for clinical manufacturing [WEBINAR]
2021年9月18日Disrupting Cell Engineering with Non-Viral Modalities
2021年5月20日Precise and Efficient Non-viral CRISPR Gene Editing Solutions for T Cell Engineering
2021年12月17日Engineered cell therapies – potential and development of non-viral methods [WEBINAR]
2020年11月17日Cutting Edge Viral and Non-Viral Delivery Platforms for T-Cell Engineering – YouTube
2020年8月5日Flexible, clinically adaptable, non-viral approaches to CAR TCR methodologies
CAR-T/CAR-NK
2025年12月5日Topic1: Lentiviral Vector Process Development for In Vivo CAR-T: Key Points and Core Challenges
2025年12月10日Webinar: A New Approach to Treating Generalized Myasthenia Gravis: KYY-101 CAR T-cell Therapy
2025年11月27日WEBINAR: ‘CAR T-cells for the treatment of hematological malignancies & solid tumours’ – YouTube
2025年9月19日Around the World: How U.S. Science is Impacting Cell and Gene Therapy
2025年3月13日Exploring CAR-T cell therapy and Auto-immune Diseases
2025年1月25日The Future of Precision Medicine: Stem Cells, Gene Therapy, and AI
2025年3月18日CARTCell Targeting Enhancements
2025年8月9日Resetting Immunity: The Power of CAR-T Therapy with Dr. Carl June @ The Cure JM Family Conference
2025年6月22日Establishing a Non-Viral Manufacturing Process for Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Therapies
the Emily Whitehead Foundation:https://www.youtube.com
The girl whose T cells beat cancer: https://www.youtube.com
2022年5月3日2022 WMIF | The Dr. Is In | Smart Materials: Non-viral Vectors for Gene Therapy
*2024年11月12日CAR T-cell Therapy: An Emerging Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases
2024年10月2日Realizing the CAR T Potential in Myositis & Beyond
2024年10月10日Genome Engineering for Rare Diseases, 2024
2024年11月26日“The Promise of T cell Engineering” – Dr. Michel Sadelain
2024年10月30日Advancing the Development of Gene Therapy for Rare Diseases Center for Individualized Medicine 2024
2024年8月21日Congressional Briefing: How Gene Therapies are Transforming the Hemophilia Landscape
2024年9月5日All About Gene Therapy
2024年5月10日Quality of Life after CAR T-cell Therapy
2022年3月1日Lunch & Learn: Gene Therapy 101
2023年5月12日Laura Sepp Lorenzino: The Promise of CRISPR Therapeutics In Vivo and Cell Therapy Applications
2023年5月2日Lunch + Learn: Intro to Non-Viral Vectors – YouTube
2021年12月22日CAR-T Cell Therapy: Now and in 2030 | Laboratory Medicine and Pathology in Individualized Medicine
2022年5月25日A cGMP Compatible, Non-Viral CAR T Cell Manufacturing Process – YouTube 60 minutes
2022年2月9日Non-viral T cell engineering for clinical manufacturing [WEBINAR] – YouTube 60 minutes
2023年2月3日A 2023 Update on CAR-T Therapy in Myeloma with Dr. Craig Hofmeister – YouTube 63′
CAR T-cell Therapy: The Good, The Bad and The Long-Term 2022 – YouTube 60′
CAR T Immunotherapies-Engineering Cell Fitness: TET2-disrupted CAR T cells – YouTube 28′
New treatment horizon : Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR T Cell Therapy – YouTube 66′
Therapeutic T cell engineering: CD19 CAR therapy and beyond, Center for Cell Engineering, NY 40′
Science Spotlight – CAR T Cells: On the Road to Synthetic Immunity | Memorial Sloan Kettering 62′
CAR T-cell Therapy in Multiple Myeloma 52′
Understanding CAR T-cell therapy (November 2020) 68
Immuno Oncology Scientific Updates Webcast Tumor Mutational Burden 52
Update on CAR T Cell Therapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma | LRF Webinars 62
CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy for Pediatric ALL: The Seattle Children’s Experience 57
Chimeric Antigen Receptors: From proof of concept to widely applicable clinical research solutions 52
Structure-Function Relationship in Chimeric Antigen Receptors – Maksim Mamonkin 30
Genome
CGC Webinar – March 2023 – YouTube 60
DNA damage: Dr Stephen J Elledge – YouTube 38′
Complete ChatGPT Tutorial – [Become A Power User in 30 Minutes] – YouTube, 30 minutes
Genome: Unlocking Life’s Code – YouTube, 120 minutes
6.047/6.878 Lecture 18 – Genome Evolution (Fall 2020) – YouTube 90 minutes
CARTA: The Evolution of Human Biodiversity: Evan Eichler -Genome Structural Variation – YouTube 30 minutes
CRISPR Biology and the New Era of Genome Engineering – YouTube 90 minutes
Regulatory and Epigenetic Landscapes of Mammalian Genomes – Laura Elnitski (2012) – YouTube 73 minutes
Sergey Koren: A Complete Diploid Human Genome – YouTube 60 minutes
Bjorn Schumacher, Genome Stability in Aging and disease – YouTube , 26 minutes
Human Genome Project & The DNA Molecule Explained – YouTube 42 minutes
How Genome Size Constrains Plant Ecology and Distribution | Andrew Leitch – YouTube 70 minutes
Molecular biology and Techniques
Molecular Biology #1 2020 – YouTube 90′
Molecular Biology #2 2020 – YouTube 68′
Molecular Biology #3 2020 – YouTube 90′
Molecular Biology #4 2020 – YouTube 90′
Molecular Biology Techniques – YouTube 200′
BioM01 Molecular Biology 2021 2022 Structure of nucleic acids – YouTube 72′
MED LEVEL 1 GEN BIO Lecture of Molecular Biology techniques 1,MTI 2022 – YouTube 26′
Basic Molecular Biology Research Techniques – YouTube 68′
Molecular Biology Techniques – YouTube 71′
Experimental Techniques in Molecular Biology, Part I – YouTube 56′
Epigenetics
Science on the Grand 2019 Keynote: Epigenetics and Future Scientists – YouTube 37′
Trauma’s Effect on the Lifecourse: An overview of epigenetics – YouTube 51′
Keynote: How Chromatin organization and epigenetics talk with… – Gil Ast – ISMB/ECCB 2013 – YouTube 57′
What is epigenetic and why knowing it will change your life ? – Dr Moshe Szyf – YouTube 60′
Epigenetic inheritance – health and lifestyle across the generations – YouTube 52′
Genomic Imprinting and Mammalian Evolution | Azim Surani, Gurdon Institute Cambridge, UK – YouTube 63′
Karin B. Michels | Is Epigenetics Inherited? || Radcliffe Institute – YouTube 44′
What is Epigenetics? – with Nessa Carey – YouTube 40′
Howard Chang (Stanford, HHMI) 1: Epigenomic Technologies – YouTube 40′
Howard Chang (Stanford, HHMI) 2: LncRNA Function at the RNA Level: Xist – YouTube 24′
Howard Chang (Stanford, HHMI) 3: LncRNA Function at the DNA Level: PVT1 – YouTube 23′
C. David Allis (Rockefeller U.) 1: Epigenetics: Why Your DNA Isn’t Enough – YouTube 42′
C. David Allis (Rockefeller U.) 2: Epigenetics in Development and Disease – YouTube 45′
Basic biology
2025年3月12日 Rewriting DNA to make custom monstrosities – YouTube
Directed Evolution