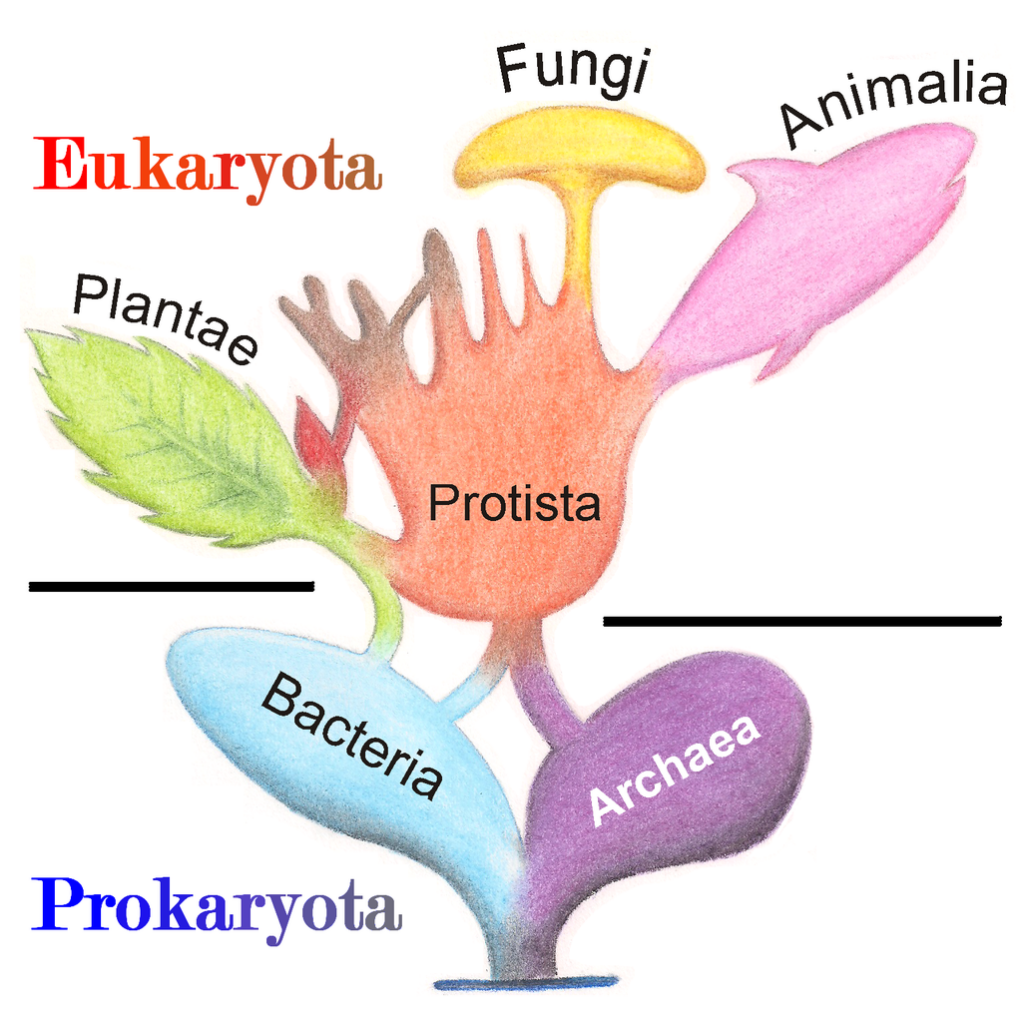
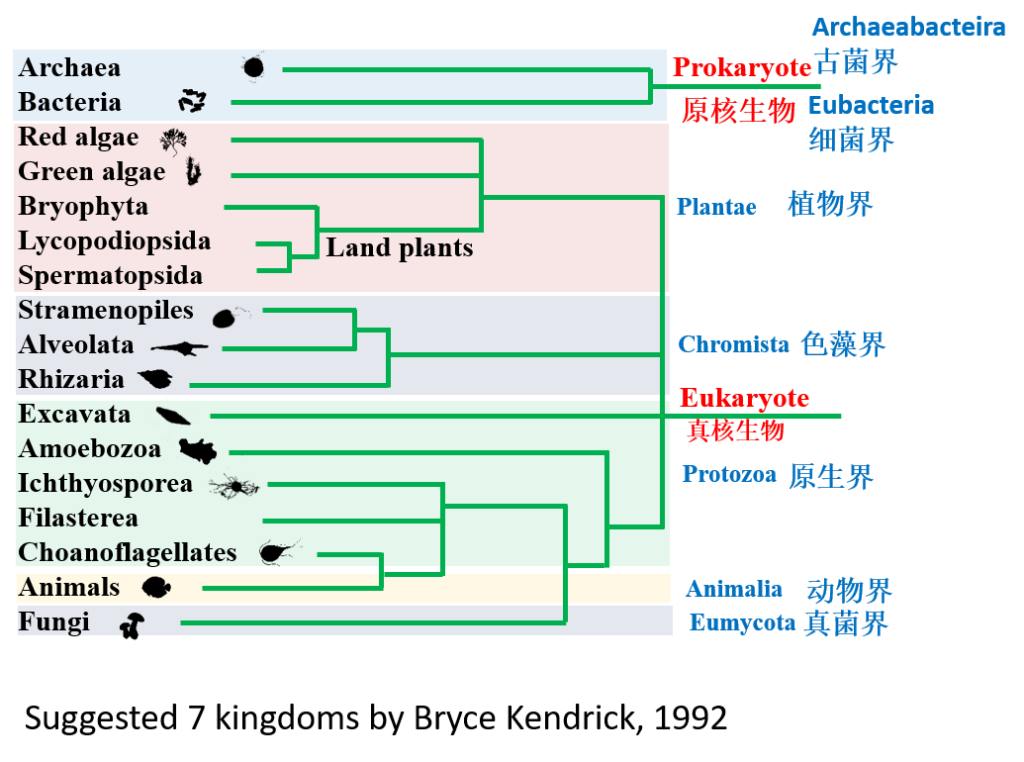
Kingdoms
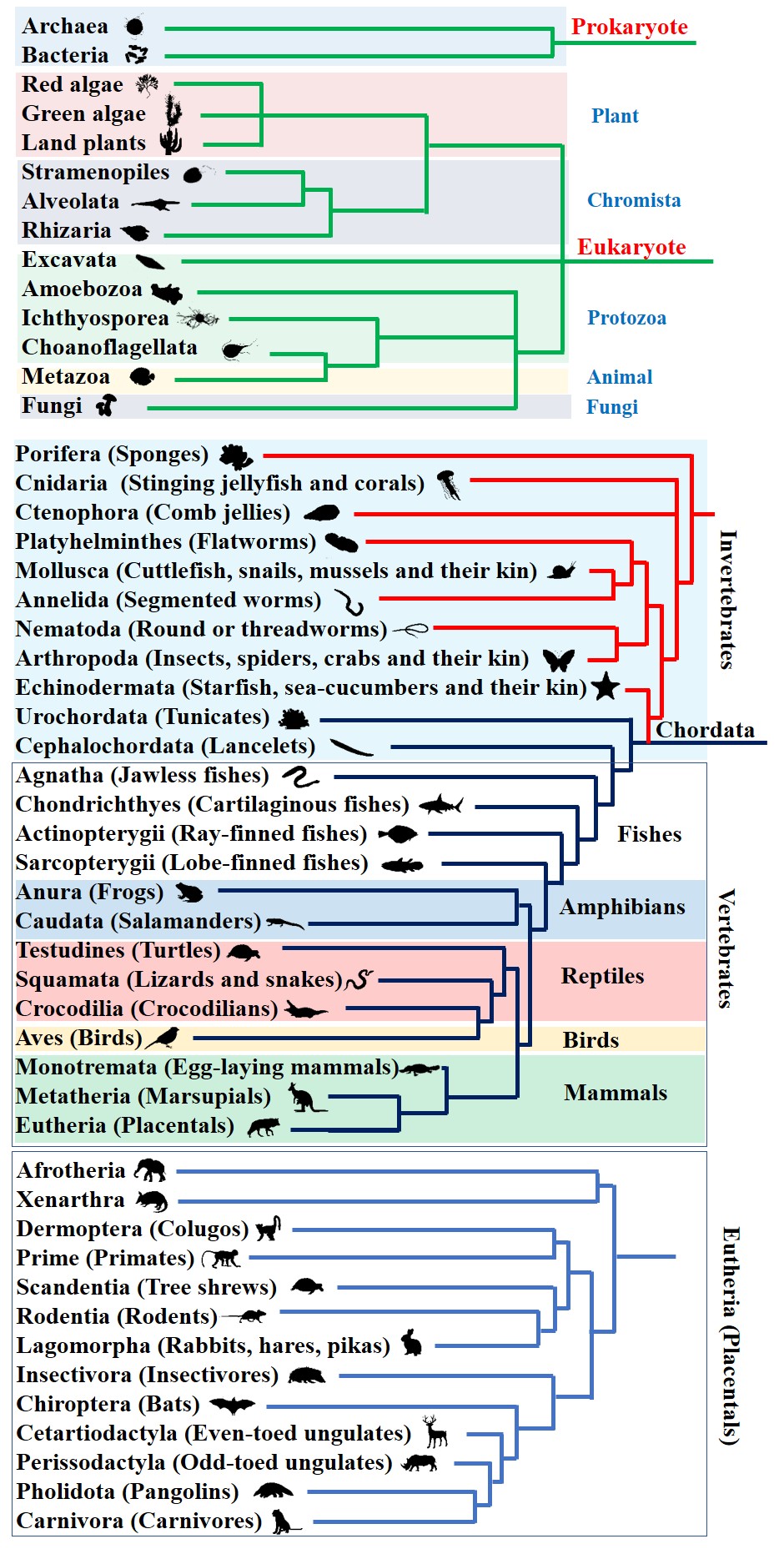
Animals
| Phylum | Described species | Land | Sea | Freshwater | Free-living | Parasitic |
| Arthropoda | 1,257,000[70] |
1,000,000 (insects)[78] |
>40,000 (Malac- ostraca)[79] | 94,000[71] | Yes[72] | >45,000[c][73] |
| Mollusca |
85,000[70] 107,000[80] | 35,000[80] | 60,000[80] |
5,000[71] 12,000[80] | Yes[72] | >5,600[73] |
| Chordata | >70,000[70][81] | 23,000[82] | 13,000[82] |
18,000[71] 9,000[82] | Yes |
40 (catfish)[83][73] |
| Platyhelminthes | 29,500[70] | Yes[84] | Yes[72] | 1,300[71] | Yes[72] 3,000–6,500[85] | >40,000[73] 4,000–25,000[85] |
| Nematoda | 25,000[70] | Yes (soil)[72] | 4,000[74] | 2,000[71] | 11,000[74] | 14,000[74] |
| Annelida | 17,000[70] | Yes (soil)[72] | Yes[72] | 1,750[71] | Yes | 400[73] |
| Cnidaria | 16,000[70] | Yes[72] | Yes (few)[72] | Yes[72] |
>1,350 (Myxozoa)[73] | |
| Porifera | 10,800[70] | Yes[72] | 200–300[71] | Yes | Yes[86] | |
| Echinodermata | 7,500[70] | 7,500[70] | Yes[72] | |||
| Bryozoa | 6,000[70] | Yes[72] | 60–80[71] | Yes | ||
| Rotifera | 2,000[70] | >400[87] | 2,000[71] | Yes | ||
| Nemertea | 1,350[88][89] | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Tardigrada | 1,335[70] |
Yes[90] (moist plants) | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Gastrotricha | 794[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | Yes | ||
| Xenacoelomorpha | 430[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Nematomorpha | 354[70] |
Yes (moist places)[90] |
Yes (one genus)[91] | Yes |
Yes (as adults)[90] |
Yes (as juveniles)[90] |
| Brachiopoda |
396[70] (30,000 extinct)[90] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Kinorhyncha | 196[70] | Yes (mud)[90] | Yes | |||
| Ctenophora | 187[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Onychophora | 187[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Chaetognatha | 186[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Entoprocta | 172[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | Yes | ||
| Hemichordata | 126[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Rhombozoa | 107[70] | Yes | ||||
| Gnathostomulida | 97[70] | Yes (sand)[90] | Yes | |||
| Loricifera | 30[70] | Yes (sand)[90] | Yes | |||
| Orthonectida | 29[70] | Yes | ||||
| Priapulida | 20[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Phoronida | 16[70] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Placozoa | 4[92] | Yes[90] | Yes | |||
| Cycliophora | 2[93] | Yes[93] | Yes[94][93] | |||
| Micrognathozoa | One[90] | Yes (sand)[90] | Yes |
Invertebrate groups:
Annelids
Arachnids
Crustaceans
Echinoderms
Flatworms
Insects
Molluscs
Nematodes
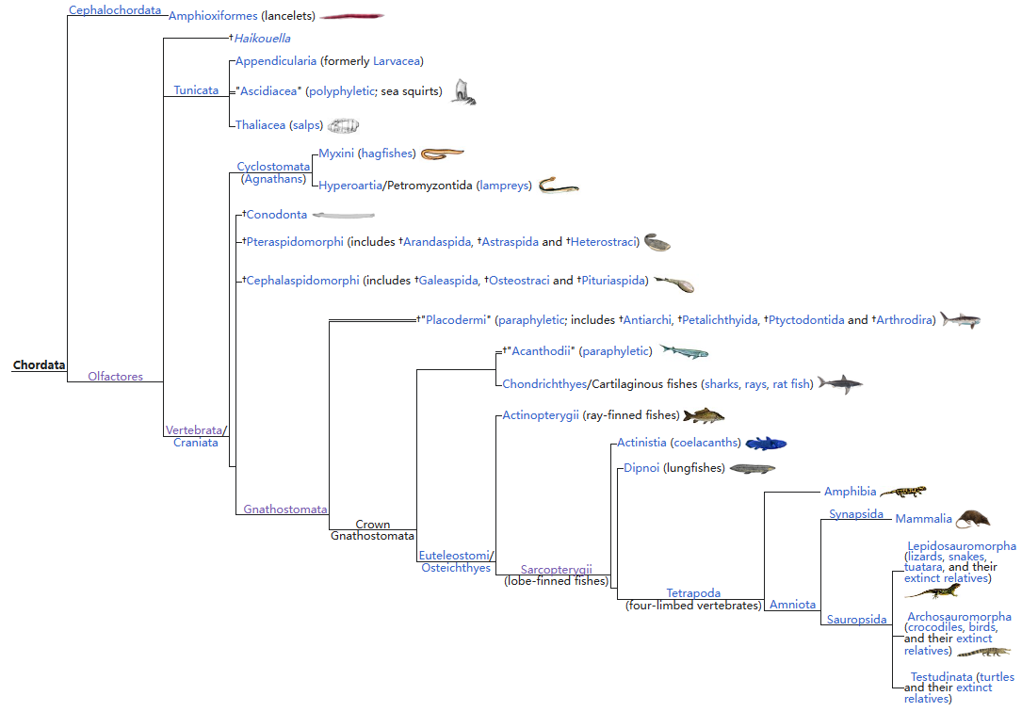
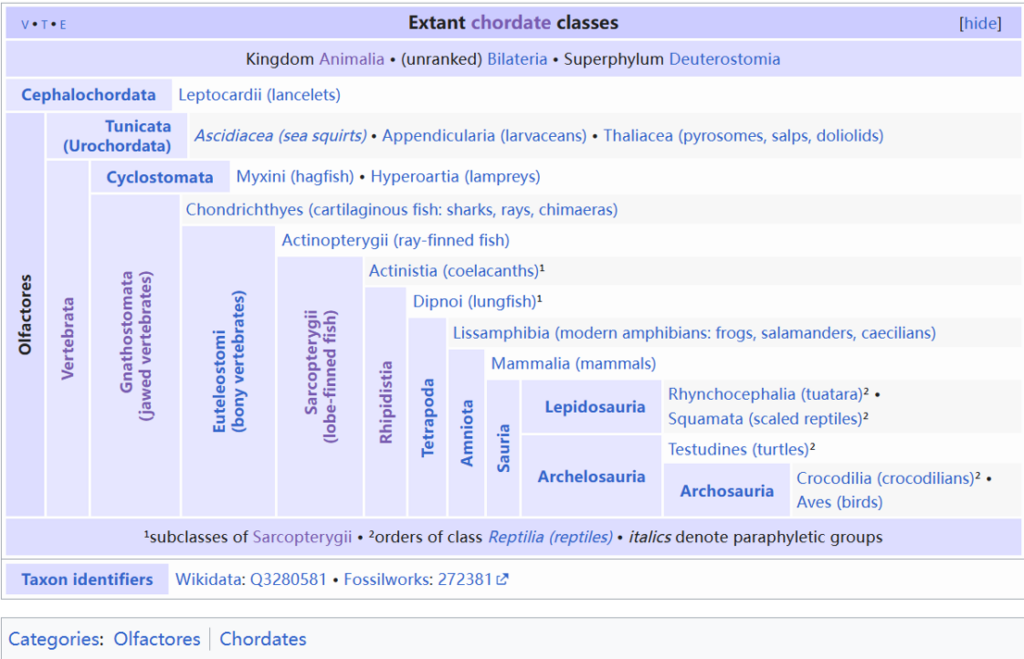
Chordata
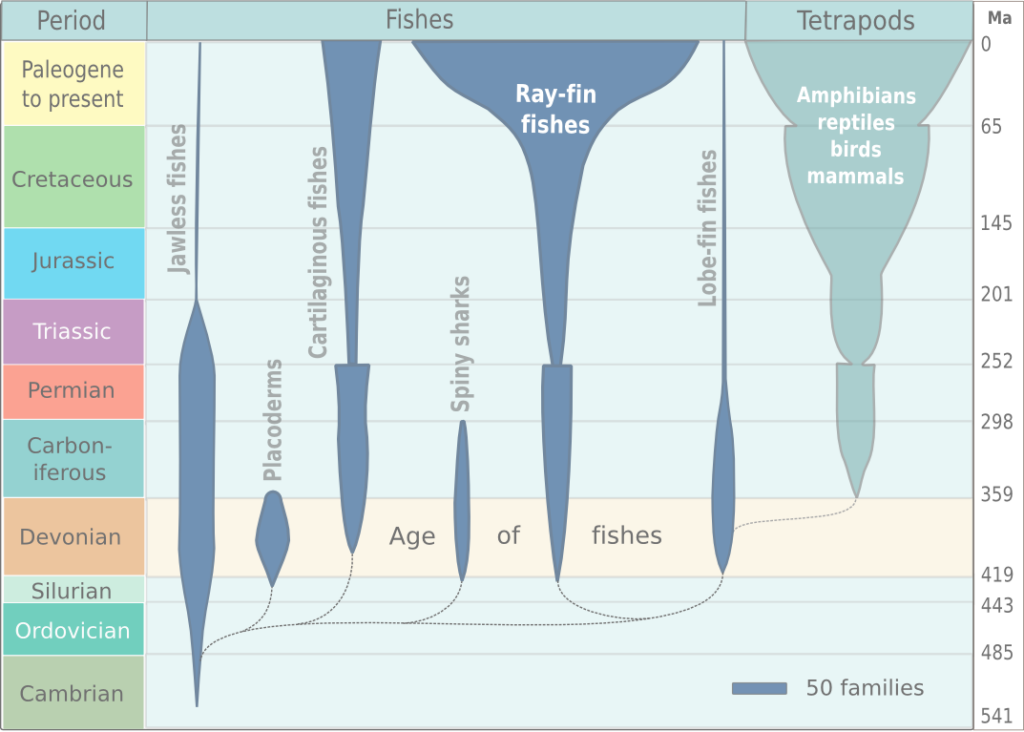
Fish evolution
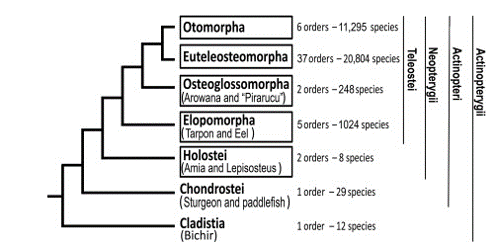
Divergent Genomes of Teleosts
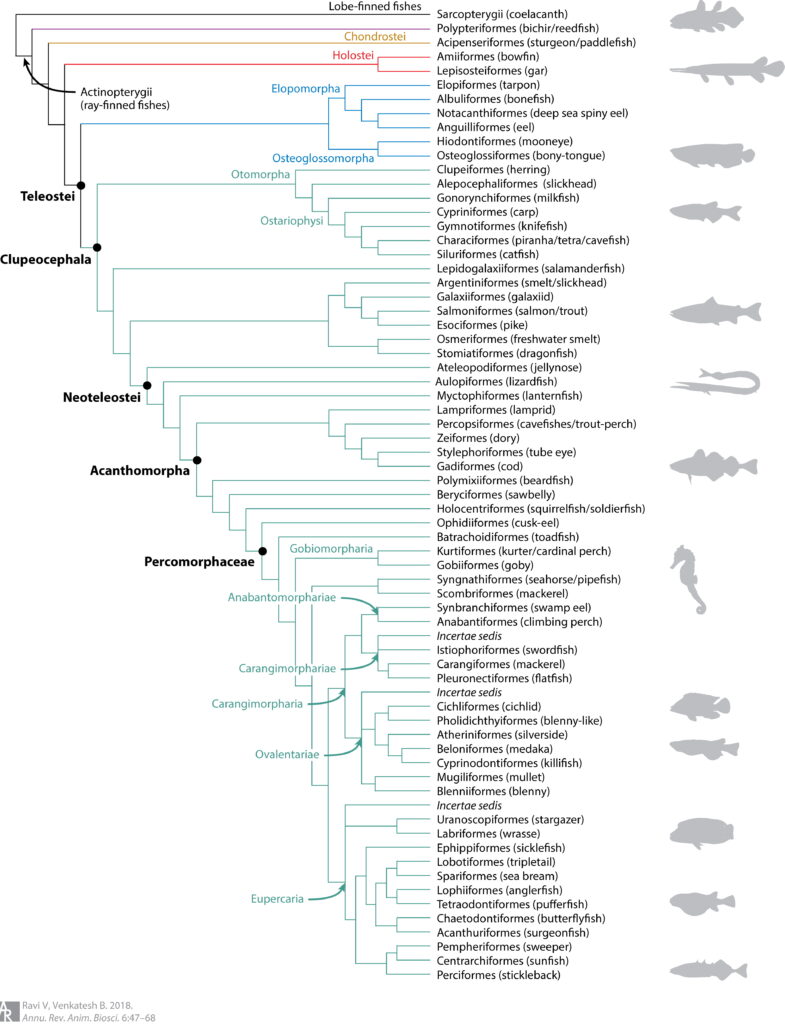
300 Actinopterygians (blue and red) and three sarcopterygian outgroups (green) with divergence dates estimated
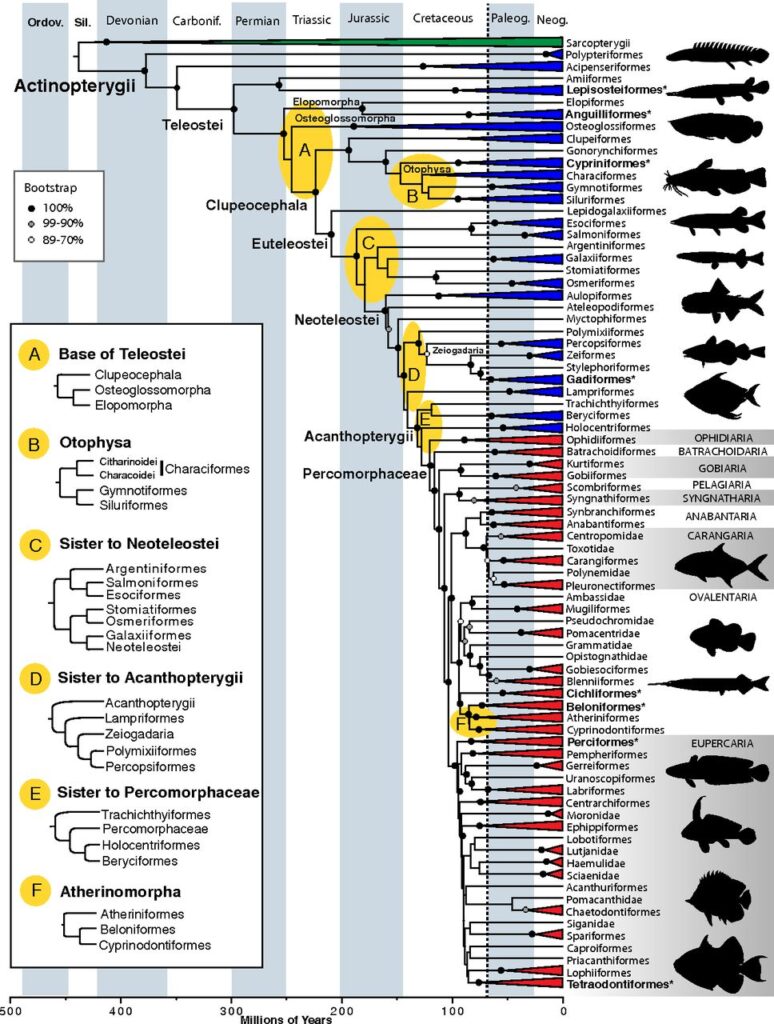
Chronogram with divergence times estimated
Phylogeny of Actinopterygii